- What happened at Route 50 and County Line Road
- Agencies involved and how to obtain official records
- Illinois civil law after a fatal or severe crash
- How liability may be investigated in a van vs. semi collision
- Insurance coverage that may apply
- Steps to protect rights and preserve evidence
- Roadway safety and intersection risk context
- Supportive services and practical help
- Commentary from Gosuits Peotone, Illinois Personal Injury Attorney
- Why timely action matters
What happened at Route 50 and County Line Road
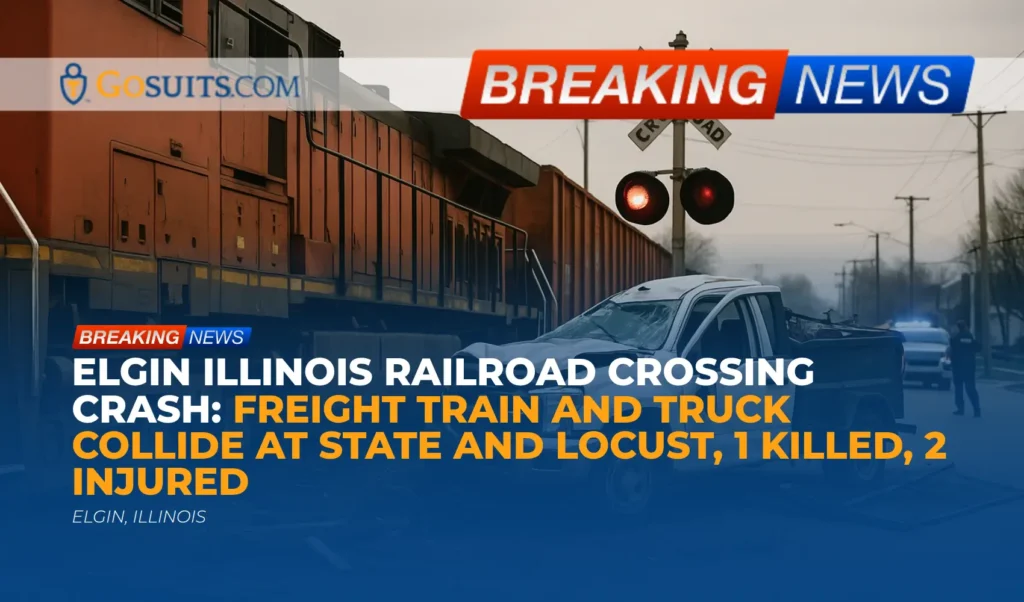
Officials reported a serious two-vehicle collision at the intersection of Route 50 and County Line Road in Peotone, Will County, on Friday at approximately 7:35 p.m. Responders from the Manhattan Fire Protection District arrived to find a van and a semi-truck with significant damage. Seven people were trapped in the van. After a complex extrication, six occupants were transported to nearby hospitals, with two listed in critical condition. One person was pronounced dead at the scene, and a second critically injured individual later died at the hospital. A child was airlifted to Comer Children’s Hospital in Chicago. The Will County Coroner identified one of the deceased as a 35-year-old passenger from Aurora, who was pronounced at 9:50 p.m. The conditions of the remaining occupants were not disclosed at the time of the public updates.
Fire officials emphasized that this intersection has been the site of previous serious and fatal incidents, noting ongoing safety concerns and cooperation with legislators and local agencies to expedite safety improvements. Illinois State Police remained on scene for several hours to investigate. The cause of the crash remains under investigation.
Agencies involved and how to obtain official records
After a serious crash, official records help families understand what happened and begin any civil claim process. Below are common records and where they typically come from, with links to government resources describing how requests generally work in Illinois. Availability and timing can vary depending on the ongoing investigation.
Police crash report
Crashes on state routes in this area are commonly investigated by the Illinois State Police. Illinois State Police provide information on how to obtain traffic crash reports. Requests often require basic details such as the crash date, location, and involved vehicles. For statewide guidance, see the Illinois State Police Crash Reports portal at https://isp.illinois.gov/CrashReports.
Families sometimes also seek supplemental documents developed during the investigation, such as photographs or diagram pages. Those materials, if not part of the standard report, may be requested under the Illinois Freedom of Information Act, discussed below. Release timing may be delayed while investigations remain open.
Fire department and EMS incident records
Local fire protection districts and EMS providers create their own run reports documenting extrication and care. In Illinois, records held by public bodies can be requested under the Freedom of Information Act. See the State of Illinois FOIA guidance at https://www2.illinois.gov/sites/foia/Pages/default.aspx. When requesting, include the incident date, time, location, and any known run number. Some medical details are protected by privacy laws and may require proof of authority by a legal representative or next of kin.
Coroner reports and autopsy
In fatal incidents, county coroners typically determine cause and manner of death and maintain related records. Each county coroner’s office sets procedures for releasing reports to next of kin or authorized representatives. While procedures are local, Illinois death certificates are managed through the Illinois Department of Public Health Vital Records. Guidance on obtaining death records is at https://dph.illinois.gov/topics-services/birth-death-other-records.html. Coroner reports are separate from death certificates and are obtained from the county coroner’s office. If you are unsure how to request, contacting the office by phone can help clarify the process and the documentation required.
Medical records for those injured
Hospitals and treating providers maintain medical records and billing statements. Federal rules explain your rights to access medical records. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services provides guidance here: https://www.hhs.gov/hipaa/for-individuals/medical-records/index.html. If the patient is a minor or is incapacitated, a parent or court-appointed representative may need to request records on their behalf.
Using Illinois FOIA for investigative materials
Illinois FOIA provides a path to request public records from state and local agencies. Not all materials are subject to release, and active investigations may delay disclosure. The state’s FOIA overview, with agency contact information, is at https://www2.illinois.gov/sites/foia/Pages/default.aspx. Requests should be as specific as possible and may include police narratives, crash diagrams, 911 audio, or dispatch logs, recognizing that certain exemptions and privacy protections apply.
Illinois civil law after a fatal or severe crash
When a crash results in serious injury or loss of life, Illinois law provides civil pathways for families and injured survivors to seek accountability and compensation for harms. Because every situation is different, the points below are general information intended to help the community understand the framework that may apply.
Wrongful death and survival actions
Illinois recognizes two related civil claims in fatal cases. A claim under the Illinois Wrongful Death Act addresses losses suffered by the surviving spouse and next of kin, such as grief, loss of companionship, and support. See 740 ILCS 180/2 at https://www.ilga.gov/legislation/ilcs/ilcs3.asp?ActID=2034&ChapterID=56. A claim under the Survival Act preserves certain claims the decedent could have brought if they had lived, such as conscious pain and suffering and medical expenses, and becomes part of the estate. See 755 ILCS 5/27-6 at https://www.ilga.gov/legislation/ilcs/ilcs3.asp?ActID=2104&ChapterID=60.
Who may bring the claim
Wrongful death claims are generally brought by the personal representative of the decedent’s estate for the benefit of the surviving spouse and next of kin, as specified in the statute. The probate court can appoint a representative if one has not already been named.
Time limits
Illinois law sets filing deadlines. Many wrongful death cases must be filed within two years of death under 740 ILCS 180/2. See the statute at https://www.ilga.gov/legislation/ilcs/ilcs3.asp?ActID=2034&ChapterID=56. General personal injury claims are subject to a two-year period under 735 ILCS 5/13-202 at https://www.ilga.gov/legislation/ilcs/documents/073500050k13-202.htm. Claims against certain public entities can have shorter deadlines, frequently one year under 745 ILCS 10/8-101 at https://www.ilga.gov/legislation/ilcs/ilcs3.asp?ActID=736&ChapterID=11. There are exceptions and special rules, so timeframes can vary depending on the parties involved and the facts.

Comparative fault
Illinois follows a modified comparative negligence rule. Recovery is barred if a plaintiff is more than 50 percent at fault, and otherwise reduced in proportion to fault. See 735 ILCS 5/2-1116 at https://www.ilga.gov/legislation/ilcs/documents/073500050k2-1116.htm. In multi-vehicle collisions, fault may be allocated among multiple drivers or entities based on the evidence.
How liability may be investigated in a van vs. semi collision
Crashes involving large commercial trucks raise unique investigative issues. A thorough civil investigation often considers the following, coordinated with the official law enforcement investigation:
- Driver hours and fatigue. Federal hours-of-service rules limit the number of hours commercial drivers may drive and work, with electronic logging devices to document compliance. See 49 CFR Part 395 at https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-49/subtitle-B/chapter-III/subchapter-B/part-395. Fatigue can impair reaction time and decision-making.
- Vehicle inspection, maintenance, and repair. Carriers must systematically inspect and maintain vehicles, with records kept for prescribed periods. See 49 CFR Part 396 at https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-49/subtitle-B/chapter-III/subchapter-B/part-396. Brake condition, lighting, and tires can be critical in crash causation and severity.
- Event data recorder and telematics. Many vehicles store pre-crash data about speed, braking, throttle, and seat belt status in electronic modules. NHTSA provides background on event data recorders at https://www.nhtsa.gov/research-data/event-data-recorder. Prompt preservation helps avoid loss of this evidence.
- Intersection design and control. Sight lines, signage, signal timing, and turn lanes influence conflicts between vehicles. Intersection-related risk and treatment strategies are discussed by the Federal Highway Administration at https://safety.fhwa.dot.gov/intersection/.
- Compliance with traffic control and right-of-way. Whether vehicles obeyed signals, signs, and right-of-way rules is central. Physical evidence such as skid marks, debris fields, and vehicle rest positions, combined with eyewitness statements and video if available, inform these findings.
- Carrier oversight and supervision. Beyond a driver’s conduct, a motor carrier’s hiring, training, and supervision may be examined for systemic issues that contributed to the crash.
In a complex crash with multiple occupants and serious injuries, it is common for several insurance carriers and investigators to be involved. Careful coordination helps ensure key materials are preserved while respecting the official investigation led by Illinois State Police.
Insurance coverage that may apply
Several layers of insurance may be implicated in a van versus semi-truck collision. Each policy has its own terms and notice requirements, and the order of coverage can depend on fault, vehicle ownership, and occupancy.
- Commercial motor carrier liability insurance. Interstate motor carriers are required to maintain minimum financial responsibility under federal regulations, often between $750,000 and $5,000,000 depending on the cargo. See 49 CFR Part 387 at https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-49/subtitle-B/chapter-III/subchapter-B/part-387. Higher limits may exist depending on the carrier and policy.
- Van owner’s liability coverage. The policy covering the van may apply for injuries to passengers and others, subject to the facts and Illinois law on fault allocation.
- Uninsured and underinsured motorist coverage. Illinois auto policies often include UM and UIM for injuries caused by drivers who lack insurance or do not carry enough. The Illinois Department of Insurance provides consumer information about auto coverages and claims processes at https://insurance.illinois.gov.
- Medical payments coverage. Some policies include optional medical payments coverage that can help with medical expenses regardless of fault, up to the policy limit. Availability and terms vary by policy.
- Health insurance and hospital liens. When health insurance pays bills, subrogation and lien rules can affect how any later recovery is allocated. Hospitals in Illinois may assert liens for care related to injuries.
If insurance companies reach out early for recorded statements or authorizations, it is wise to proceed carefully. What is said to an insurer can be used later in claim evaluation. Before engaging with insurers, consider speaking with a qualified attorney in a free consultation to understand rights and obligations under the policies.
Steps to protect rights and preserve evidence
In the immediate aftermath of a serious collision, families and injured survivors face urgent medical and personal concerns. The civil process does not need to take priority over healing, but certain steps can help protect the ability to learn the full truth and pursue accountability if appropriate.
- Speak with an attorney before contacting insurance companies. Insurance adjusters may request recorded statements or broad medical authorizations. These can have significant implications. It is prudent to get a free consultation first. What is shared with an insurance company can be used against a claimant later.
- Preserve vehicles and electronic data. Ask that all vehicles be preserved until they can be inspected and photographed, including downloads of event data recorders and any telematics. Quick action is important because data can be overwritten when vehicles are moved or repaired. NHTSA’s background on event data recorders is at https://www.nhtsa.gov/research-data/event-data-recorder.
- Request official reports promptly. Obtain the Illinois State Police crash report when available from https://isp.illinois.gov/CrashReports. Consider FOIA requests for dispatch logs, 911 audio, and photos once the investigation allows. Illinois FOIA overview is at https://www2.illinois.gov/sites/foia/Pages/default.aspx.
- Collect medical and expense documentation. Keep discharge summaries, physician notes, prescriptions, therapy plans, travel costs, and wage information for missed work. HHS guidance on medical record access is here: https://www.hhs.gov/hipaa/for-individuals/medical-records/index.html.
- Identify witnesses and potential video. Note names, phone numbers, and any businesses or residences near the intersection that may have cameras. Many systems overwrite footage in days, so early inquiries matter.
- Be mindful of filing deadlines. Illinois statutes impose time limits for wrongful death and personal injury claims, and different rules can apply when public entities are involved. See 740 ILCS 180/2 at https://www.ilga.gov/legislation/ilcs/ilcs3.asp?ActID=2034&ChapterID=56 and 745 ILCS 10/8-101 at https://www.ilga.gov/legislation/ilcs/ilcs3.asp?ActID=736&ChapterID=11.
Roadway safety and intersection risk context
Intersection crashes are a significant source of severe injuries nationwide. The Federal Highway Administration highlights proven strategies to reduce intersection crashes, including better sight distance, enhanced warning signs, improved signal timing, protected turn phases, and roundabouts where appropriate. See FHWA’s intersection safety resources at https://safety.fhwa.dot.gov/intersection/.
Nationally, transportation safety agencies stress the importance of engineering, enforcement, and education working together. While the specific cause of the Peotone crash remains under investigation, the observation by local fire officials that the Route 50 and County Line Road intersection has seen multiple serious incidents underscores the value of timely safety assessments. The Illinois Department of Transportation’s safety program describes planning and funding processes for systemic improvements through programs like the Highway Safety Improvement Program, available at https://idot.illinois.gov/transportation-system/safety/highway-safety-improvement-program.
For families, it is helpful to know that safety reviews can run on parallel tracks with individual civil claims. Findings about sight lines, signage, lighting, and traffic volumes can be relevant to understanding how a crash happened and whether roadway conditions contributed.
Supportive services and practical help
In the days following a traumatic event, balancing logistics with grief and recovery is difficult. The following resources and steps can help organize needs and ensure that essential documents are obtained.
Where to call for key documents
- Illinois State Police crash report: Follow instructions at https://isp.illinois.gov/CrashReports. Have the crash date, location, and vehicle details ready. If uncertain which district handled the scene, the ISP portal provides guidance.
- Coroner records: Contact the county coroner’s office for autopsy and investigative reports. Each coroner sets procedures for next-of-kin access and any fees. Have identification and proof of relationship available.
- Death certificates: Illinois Department of Public Health outlines how to request death records at https://dph.illinois.gov/topics-services/birth-death-other-records.html. Funeral homes can often assist with initial copies.
- Fire and EMS run reports: Submit a written request to the local fire protection district or EMS provider. For public bodies, see Illinois FOIA overview at https://www2.illinois.gov/sites/foia/Pages/default.aspx.
- Hospital records and bills: Request through each hospital’s Health Information Management department. HHS explains patient access rights at https://www.hhs.gov/hipaa/for-individuals/medical-records/index.html.
Emotional support and crisis care
- National mental health support: The SAMHSA National Helpline provides free, confidential support and referrals for mental health and substance use 24 hours a day. See https://www.samhsa.gov/find-help/national-helpline.
- Local victim support: County and state agencies may offer counseling and victim assistance. Ask hospitals, law enforcement victim services, or county social services for local referrals.

Organizing information
Keep a single folder for all crash-related documents, including a timeline of events, names and contact information of witnesses, claim numbers from any insurers, and copies of expenses such as travel for medical care, medications, and time away from work. This organization helps medical providers, insurers, and any legal team understand the full picture.
Commentary from Gosuits Peotone, Illinois Personal Injury Attorney
Our hearts are with everyone affected by the devastating collision at Route 50 and County Line Road. Losing a loved one or seeing a family member in critical condition is a profound hardship. This article is intended to share general information and context for our community while the official investigation continues.
Crashes at rural and semi-rural intersections can be complex. When a van carrying multiple occupants collides with a semi-truck, the forces involved are severe, and the stakes for families are immense. From a civil perspective, the focus turns to a careful reconstruction of how the collision occurred. That includes driver conduct, compliance with traffic control, visibility at the intersection, and whether any systemic safety issues contributed. With multiple victims and two fatalities reported, a thorough, well-documented investigation is essential.
It is also important to recognize how large insurance companies and corporate carriers approach these events. They move quickly, deploying adjusters and investigators to shape the narrative and gather statements. Early conversations can seem routine, yet they influence how claims are evaluated. People without guidance can feel pressured to give recorded statements or sign broad medical authorizations that later limit their options. Understanding policy obligations and the sequence of coverage in multi-vehicle crashes helps balance the playing field.
A free consultation can provide clarity on practical next steps, preservation of evidence, and which timelines apply. Families do not have to navigate insurance communications, FOIA requests, and medical record gathering alone. Speaking with a seasoned attorney early does not commit anyone to a particular course. It helps ensure that decisions made in the first days and weeks do not unintentionally harm future options.
Why timely action matters
When a serious crash occurs, several clocks start running. Understanding them adds urgency and direction to the response:
- Evidence can disappear quickly. Vehicles may be moved or disposed of, and electronic data may be overwritten. Event data recorders and commercial telematics often store only limited durations of information. Prompt preservation requests reduce the risk of losing key facts. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration explains event data recorders at https://www.nhtsa.gov/research-data/event-data-recorder.
- Regulatory record retention is limited. Federal rules require motor carriers to keep certain records, like driver duty status logs, for defined periods. For example, hours-of-service record retention is measured in months rather than years. See 49 CFR Part 395 at https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-49/subtitle-B/chapter-III/subchapter-B/part-395. Taking action early increases the chance those records are preserved.
- Medical pathways and documentation. Early follow-up care, specialist referrals, and accurate diagnoses not only aid recovery but also document the full extent of harm. HHS guidance on accessing records is here: https://www.hhs.gov/hipaa/for-individuals/medical-records/index.html.
- Insurance policy notice requirements. Auto and commercial policies commonly require prompt notice of a potential claim. Failing to give timely notice can affect coverage. Review policy documents and get clarity on notice obligations before speaking substantively with adjusters. Consider contacting an attorney first to understand these requirements and how to meet them without risking statements being used against a claimant.
- Statutory deadlines. Illinois law sets filing deadlines for wrongful death and personal injury claims, and some claims against public entities have shorter windows. See 740 ILCS 180/2 at https://www.ilga.gov/legislation/ilcs/ilcs3.asp?ActID=2034&ChapterID=56 and 745 ILCS 10/8-101 at https://www.ilga.gov/legislation/ilcs/ilcs3.asp?ActID=736&ChapterID=11. Acting within these timeframes preserves the ability to pursue a claim.
Taking organized, timely steps helps ensure the full truth can be learned and that options remain open. It does not require rushing to decisions while families are still processing shock and grief. It means safeguarding the information needed to make informed choices when the time is right.